Optimizing spatial and seasonal deployment of vaccination campaigns to eliminate wildlife rabies
Abstract
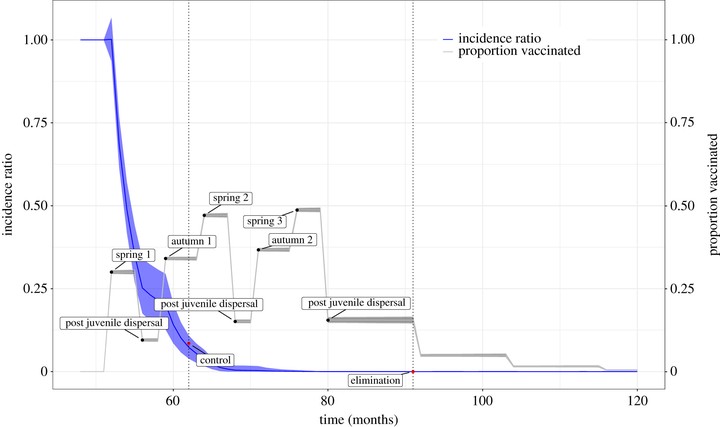
Understanding how the spatial deployment of interventions affects elimination time horizons and potential for disease re-emergence has broad application to control programmes targeting human, animal and plant pathogens. We previously developed an epidemiological model that captures the main features of rabies spread and the impacts of vaccination based on detailed records of fox rabies in eastern Germany during the implementation of an oral rabies vaccination (ORV) programme. Here, we use simulations from this fitted model to determine the best vaccination strategy, in terms of spatial placement and timing of ORV efforts, for three epidemiological scenarios representative of current situations in Europe. We found that consecutive and comprehensive twice-yearly vaccinations across all regions rapidly controlled and eliminated rabies and that the autumn campaigns had the greater impact on increasing the probability of elimination. This appears to result from the need to maintain sufficient herd immunity in the face of large birth pulses, as autumn vaccinations reach susceptible juveniles and therefore a larger proportion of the population than spring vaccinations. Incomplete vaccination compromised time to elimination requiring the same or more vaccination effort to meet similar timelines. Our results have important practical implications that could inform policies for rabies containment and elimination in Europe and elsewhere. This article is part of the theme issue ‘Modelling infectious disease outbreaks in humans, animals and plants, approaches and important themes’